Permissions can be very important when it comes to hosting your website. Permissions can allow our server computer to write and edit your files. Along with that, some files must be write and edit protected as a security measure. You can change the permissions of your files in many ways.
Using the File Manager in cPanel
One of the simple and basic ways to change permissions is through the File Manager in cPanel. To change the permissions of a file or folder in cPanel, do the following:
- Log in to cPanel.
- Click File Manager.
- There are different ways to change the permission of a file:
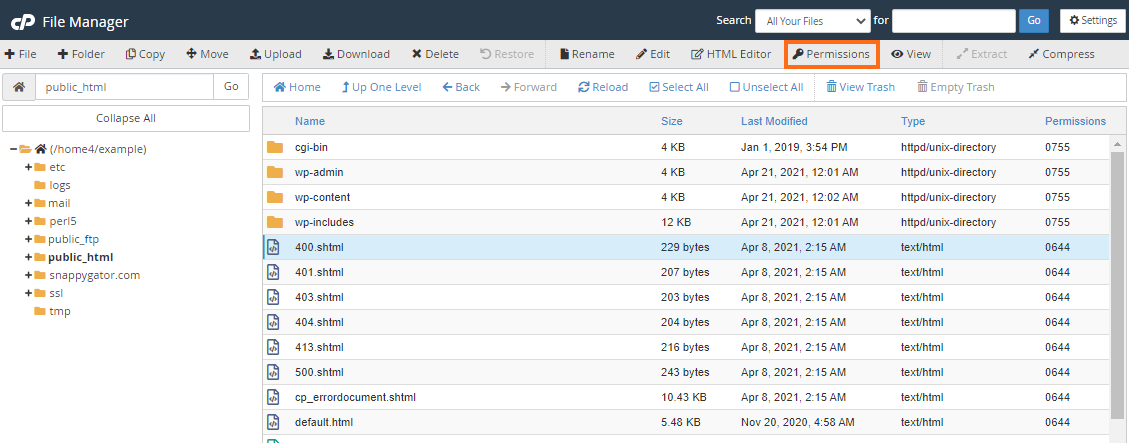
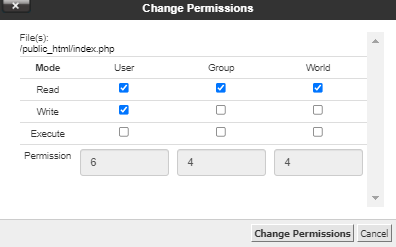
- Option 1 : Browse to and select the name of the file to which you want to change the permission. Then click on Permissions in the upper menu
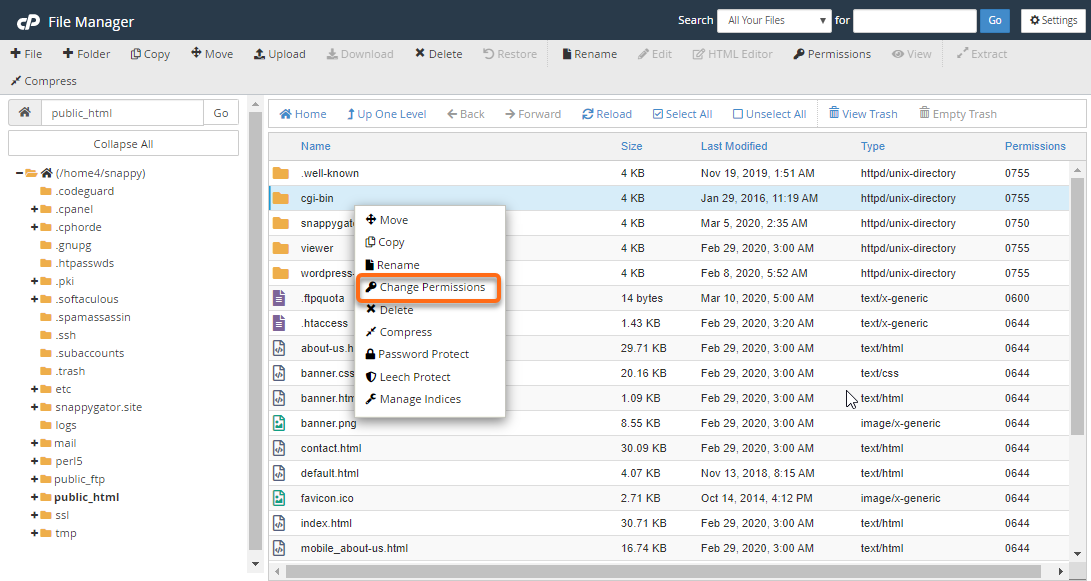
- Option 2 : Right-click on the file you want to change, then select Change permissions from the list of options.
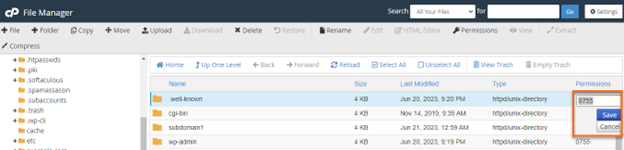
- Option 3 : double-click on the set of numbers under the Permissions column. Make changes to the permission and press Save.
- Option 1 : Browse to and select the name of the file to which you want to change the permission. Then click on Permissions in the upper menu
- Click on the check boxes to set the correct permissions.
- Click Change permissions.
Using FTP
- Start and connect to FTP .
- Browse and right-click on the file whose permissions you want to change.
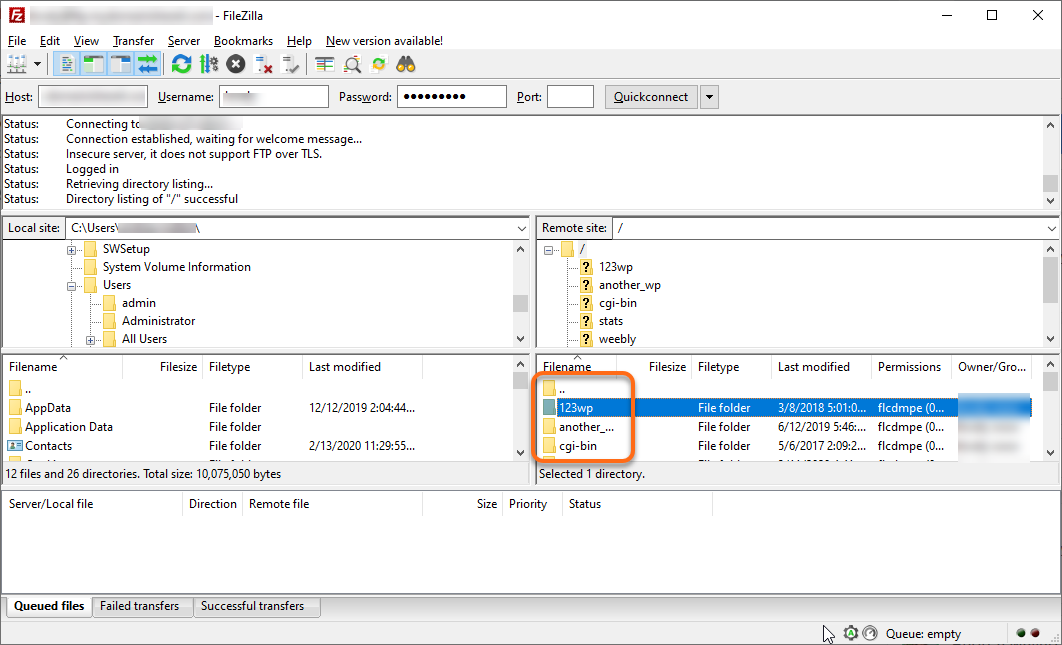
- Select File Permissions or Attributes or Properties (depending on your FTP client).
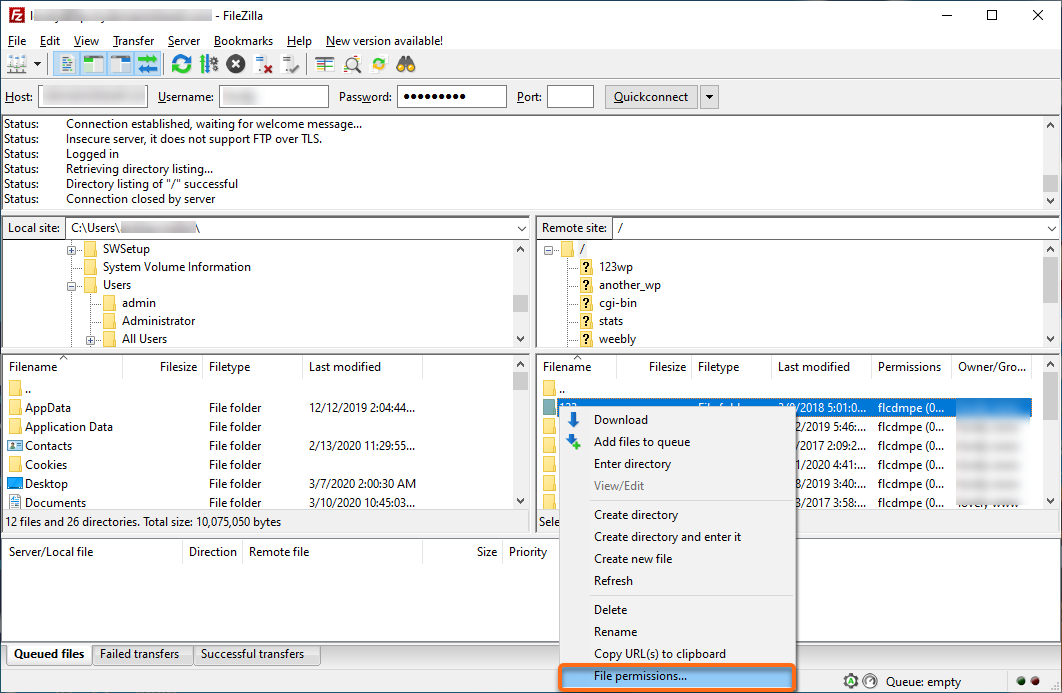
- Set the permissions you want to apply.
Using SSH or a script
This can be done with the command chmod .
So, what do these permissions and numbers mean?
File permissions determine what you can do and who can do it.
| Dueño | Grupo | Mundo | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leer | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Escribir | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ |
| Ejecutar | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
These are the three types of users.
- Owner : the owner is you, the person who has access to the cPanel or shell.
- Group: the group is other people on your server.
- World: the world is any visitor from the public (think of the world wide web).
Each row represents an action allowed for this file (or folder).
- Read means that the user can view the file.
- Write means that the user can edit the file.
- Execute means that the user can execute the file.
It is very important that Group and World can see the files on your web site. However, there are some files that you may not want anyone to see. If you remove the read mark in Group and World, the file will not show up in anyone's browser (instead, visitors will see a 403 Forbidden error).
In the File Manager, permissions are expressed as numbers. We only care about the 3 digits, so if you see 4 digits, ignore the first one. So 0755 is the same as 755.
The numbers represent a combination of each unique permission. Also, the first of the three digits represents the owner's permissions. The second digit represents the Group. The third digit represents the world.
- Read equals 4.
- Write equals 2.
- Execute equals 1.
- No permission for a user is equal to 0.
Therefore,
- Write and execute without read equals 3.
- Read and execute without write equals 5.
- Read and write without execute equals 6.
- Read and write and execute equals 7.
E
At this point, all you need to know is that your files should always have permissions of 644 or 755. (For most files, it doesn't matter whether you grant the executable permission or not. You will not see any difference).
However, folders should always be 755 .
One more rule. Any file inside the cgi-bin folder must have 755 permissions.
Advanced
A common concern is the use of file permissions of 777.
HOST does not allow 777 on files that process server-side (i.e. PHP). However, many scripts require you to change your files to 777.
I can tell you that 755 will work instead of 777. You will not need to use 777 on PHP files or folders.
What is the problem?
The concern is granting write permissions to Group and World. This allows hackers on the world wide web to edit your files. Therefore, the last two digits of file permissions should never be 2, 3, 6 or 7.
The problem is when you install a PHP script; the script needs permission to edit files. Traditionally, PHP is treated as "nobody" on the server. Therefore, PHP is treated the same as any unknown visitor and must obey the permissions granted to World.
The solution to this conflict is to treat PHP as the owner. HOST has done this by implementing a special PHP security environment known as suPHP (or phpSuExec).
With suPHP, all PHP scripts have the same permissions as the owner, and external visitors are still restricted by World permissions. Therefore, 755 is the perfect number; it allows all actions for PHP and read/view only for potential hackers.
Other formats
Permits can be expressed in many forms. You have already seen the two-dimensional array and the 3- or 4-digit numbers.
However, if you prefer to use the Linux shell (SSH), file permissions will look like this:
drwxr-xr-x
You can ignore the first character; it represents the file type rather than the permissions. Next, you will see three letters representing the owner's permissions.
- r = read
- w = write
- x = execute
- - (hyphen) = no permission
- The owner will normally have all three permissions, which are represented by rwx.
The next three characters represent the Group permissions. Finally, the last three characters represent the World permissions.
Note that Group and World do not get the write permission. In place of the 'w' there will be a hyphen, which means that you are definitely not allowed to write: rx.
Here are some conversions to consider.
| Matriz 2D | Representación numérica | Representación de Linux |
 |
755 o 0755 Recomended! |
drwxr-xr-x |
 |
644 o 0644 Recomended! |
drw-r - r-- |
 |
700 o 0700 | drwx ------ |
 |
777 o 0777 ¡ No Recomended! |
drwxrwxrwx |

